Perturbations in the environment are common, and bacterial communities consisting of several species seem to find their way around the crisis. Species immigration is beneficial for community recovery, an international study shows. Associate Professor Teppo Hiltunen from the University of Turku led the study that investigated how environmental disturbances affect the species diversity and evolution of bacterial communities.
The study was conducted using synthetic bacterial communities and antibiotics as environmental disturbances. The key finding of the study was that bacterial communities can bounce back even from high antibiotic exposures if the communities are not closed as the destroyed species can recover with immigration. The research results can be indirectly applied to increasing our understanding of mass extinction in the environment caused by human activities or the impact of antibiotic treatments on human gut microbes.
Scientists from Finland and Germany used bacteria as an example to study how communities consisting of several species respond to disturbances in their laboratory environment. Similar kinds of perturbations can occur in the human gut when antibiotic medication is applied, resulting, for example, in diarrhea. Also global warming and extreme weather conditions such as persistent drought periods can disturb many kinds of organismal communities.
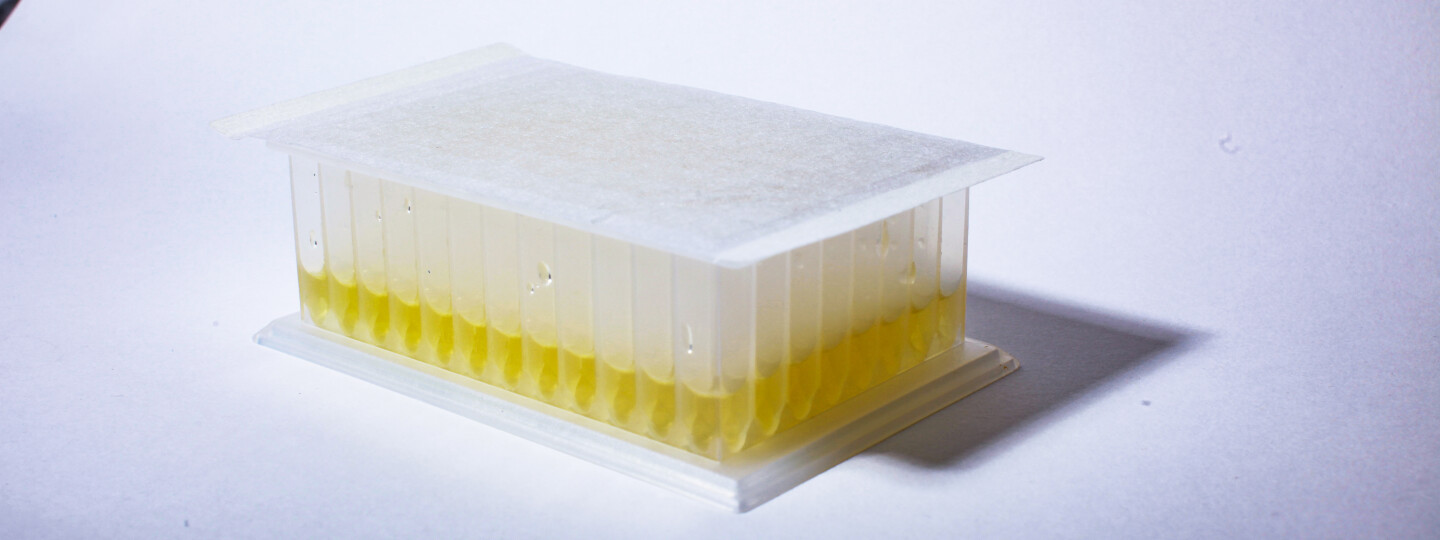
The researchers examined how a 34-species artificial bacterial community could cope with an antibiotic pulse. They used three multiplicative antibiotic levels together with an antibiotic-free control treatment.
The results show that the bacterial community changed upon antibiotic exposure, and the magnitude of the change was the bigger the higher the antibiotic level.
– However, the community recovered reasonably close to the initial state in all but the highest antibiotic level used. Even then species immigration – reintroducing a small inoculum of the original community in conjunction with each serial transfer step – enabled community recovery, says Dr. Johannes Cairns from the Bioinformatics and Evolution group at the University of Helsinki.
As a novelty, the researchers used a custom-built controlled laboratory setting with high replication. Most previous studies on the theme have been observational studies limited to the detection of associations and potentially subject to confounding environmental factors.
Another key finding of the study was that replicate communities within the same experimental treatments responded to the treatments in a relatively repeatable fashion. This could be partly explained by relevant traits, growth rate and antibiotic susceptibility, measured separately for each species in the community.
– This indicates that in certain cases the community response to perturbations may be predictable in the future, even though we could not explain the repeatability well enough to develop predictive models in this study.
The cross-disciplinary team included scientists from the University of Helsinki, University of Turku and University of Konstanz.