Sleep Research Centre
The Sleep Research Centre is a multidisciplinary research group, which is reflected in the topics of the academic dissertations. There are several ongoing research projects in co-operation with other Finnish and international research groups.
The main research interests at the centre are interactions of sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular and metabolic function, special emphasis on nocturnal transcutaneous carbon dioxide profile, and menopause, sleep and breathing.
The Sleep Research Centre also organises Sleep School once a month during the academic year under the umbrella of the Postgraduate Education Unit (PGE).
The history of the Sleep Research Centre at the Department of Physiology dates back to the 1960’s when Associate Professor Pentti Valleala carried out sleep research in animals. Sleep research in humans started in the 1970’s. In 1979, Jukka Alihanka developed the static-charge sensitive bed (SCSB). The SCSB method was further developed by Olli Polo and implemented in the diagnosis of obstructive and central sleep apnoea, partial upper airway obstruction during sleep as well as in periodic leg movements. In Finland, sleep apnoea was mostly diagnosed with the help of the SCSB until the end of the 20th century. Since 2017, Sleep Research Centre has been part of the Department of Pulmonary Diseases and Clinical Allergology.
Address: Sleep Research Unit, University of Turku, Lemminkäisenkatu 3b, FI-20520 TURKU
Personnel
Professor Tarja Saaresranta
Research Coordinator: Marjo Sunnari
Researchers
Olli Polo
Päivi Polo
Jenni Toivonen
Ulla Anttalainen
Nea Kalleinen
Salla Lamusuo
Arho Virkki
Irina Virtanen
Doctoral Candidates
Usame Al-Rammahi
Fatma Doghman
Salla Fagerudd
Jere Jaakkola
Linnea Kroneld
Olli Lyyra
Nora Nikander
Petri Ojala
Marja Palomäki
Research Projects
The Sleep Research Centre promotes co-operation and dialogue across disciplinary and institutional boundaries within the field of sleep research. Having its roots in basic physiology, the Sleep Research Centre aims at unfolding physiological mechanisms behind normal and disturbed sleep and disseminating new data in the field of sleep medicine for the benefit of medical students, health care professionals, scientists and the society.
Menopause offers a useful model to study the interactions between breathing and vascular disease. Both sleep-disordered breathing and vascular diseases increase after menopause but the effects of ageing and menopause per se are not fully understood. Premenopausal women at the age of 46 are followed up for ten years and studies will be carried out also in a cross-sectional cohort of 56-year old women.
The overall aim of the study is to clarify the interactions of nocturnal breathing abnormalities and metabolic dysfunction in middle-aged women.
The specific aims of the 5- and 10-year follow-up study are to test the effect of menopause on
- endothelial function and subclinical atherosclerosis
- sleep-disordered breathing
- sleep structure and quality, and
- daytime sleepiness
with special emphasis on nocturnal transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension profile.
Study duration 2001- Recruitment completed. Analyses and reprting ongoing.
Principal Investigator: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
ESADA (European Sleep Apnea Database) is an observational prospective real-world cohort study in collaboration between European sleep centers.
The overall aim of the ESADA project is:
- to build the largest existing database of patients with sleep and breathing disorders.
- to collect patient information from a network of European sleep centers.
- to execute cross-sectional, prospective, interventional or long-term follow-up studies based on information in the data base.
Specific study targets and objectives
Primary objective:
- to generate cross sectional data on anthropometrics, sleepiness measures and comorbidity in European patients with various degree of OSA severity.
Secondary objectives:
- to measure the incidence of cardiovascular diseases.
- to prospectively explore the cardiovascular and overall mortality in OSA and its relation to OSA severity and cardiovascular risk factors.
- to explore the effect of different OSA treatment modalities on hemodynamic and metabolic parameters as well as on cardiovascular morbidity, metabolic disorder and sleepiness.
Tertiary objectives:
- to explore the dose-response relationship between OSA severity and hypertension, hyperglycemia, cardiovascular morbidity, metabolic disorder and sleepiness.
- to assess the effect of age, gender, domicile as well as cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidity on cardiovascular endpoints in sleep apnea patients
- to assess the value of various sleep laboratory procedures in terms of diagnostic and treatment routines on outcome in sleep apnea patients.
- to assess the safety, tolerability and compliance with long-term CPAP treatment, oral devices and surgery (safety and tolerability)
European sleep laboratory clinical process evaluation
- to assess the regional differences across sleep laboratories in Europe regarding patient populations, treatment allocations, diagnostic work up, as well as adherence to therapy.
- to transfer know-how and to unify procedures as well as to generate minimum standards between different European sleep laboratories by the use of a standardized data acquisition procedure.
- to generate a data base to be used for future health economical assessments in sleep apnea patients in relation to the various national health care systems.
Substudy protocols to be generated from the joint database
- to create a network of scientifically active sleepcentres and a joint database to be used for specific patient recruitment in collaborative studies.
Recruitment, analyses and reporting ongoing.
Duration of the study: 2007-
Principal Investigator in Finland: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
Revolution of sleep diagnostics and personalized health care based on digital diagnostics and therapeutics with health data integration.
Sleep Revolution is a multidisciplinary and international research and development project funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme for Health, Demographic Change and Wellbeing, and jointly coordinated by the University of Reykjavik and the University of Eastern Finland.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with various negative health consequences including increased risk of heart disease, hypertension and daytime sleepiness causing road accidents. The economic burden of OSA is rising as almost 1 billion people worldwide are estimated to have OSA. The current diagnostic metric, however, relates poorly to these symptoms and comorbidities. It merely measures the frequency of breathing cessations without assessing OSA severity in any other physiologically relevant way. Furthermore, the clinical methods for analyzing PSG signals are outdated, expensive and laborious. Due to this, the majority of OSA patients remain without diagnosis or have an inaccurate diagnosis leading to sub-optimal treatment. Thus, it is evident that more personalized diagnostics are required including predictive and preventive health care and patient participation. The SLEEP REVOLUTION aims to develop machine learning techniques to better estimate OSA severity and treatment needs to improve health outcomes and quality of life. These techniques are implemented to high-end wearables developed in this project to alleviate the costs and increase the availability of PSGs. Finally, we aim to design a digital platform that functions as a bridge between researchers, patients and healthcare professionals. We will achieve these ambitious goals throughout extensive collaboration between sleep specialists, computer scientists and industry partners. The collaboration network consists of over 30 sleep centers working together to provide the needed retrospective data (over 10.000 sleep studies). The multi-center prospective trials involve experts and end-users to assess and validate the new SLEEP REVOLUTION diagnostic algorithms, wearables and platforms. With the commitment of the European Sleep Research Society and Assembly of National Sleep Societies (over 8000 members), we have the unique possibility to create new standardized guidelines for sleep medicine in the EU.
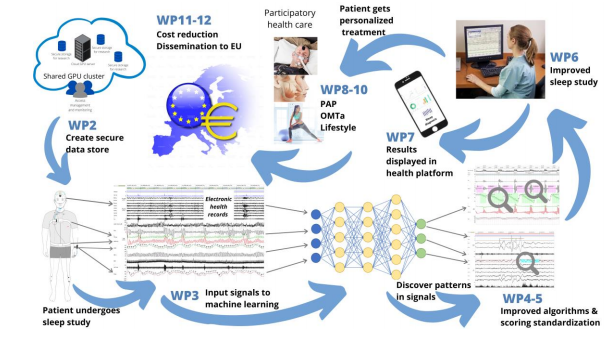
Objectives:
- Transform current diagnostic methods for sleep-disordered breathing (SDB)
- Bring advanced sleep diagnostics from hospital into patient’s home
- Promote participatory health care with technological solutions
- Develop different personalized treatment options for SDB
Duration of the study: Started March 1, 2021
Principal investigator at the University of Turku: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
Principal investigator at the Turku University Hospital: Adjunct professor Ulla Anttalainen
The data are fragmented and studies are focusing on interactions of sleep and obesity, eating pattern and obesity, or gut microbiota and obesity, but not the cross-talk of all these factors in the same individual or population. Therefore, we need a multifactorial approach to get a more deep insight on the obesity and weight regulation. Further, novel cost-effective tools to advance lifestyle changes are needed. Emerging evidence suggests that novel countermeasures, such as modulation of the timing of food intake, may be effective strategies in weight control and prevention of obesity.
Objectives:
- to provide scientific basis for the relationship between subjective sleep quality, diurnal eating pattern, gut microbiome, and obesity
- to develop and test a pragmatic, cost-effective new tool to advance lifestyle changes using E-health approach
- to compare differences in subjective sleep quality, diurnal eating pattern and gut microbiome at baseline
- to compare changes induced by the E-health intervention among the three study groups and participants with different work schedules
Participants:
- Three groups of participants will be recruited via newspaper announcements, social media, and the database of the Turku University Hospital: community dwelling 18 – 65 year old adults 1) with BMI 18.5 - 30 kg/m2 (n = 40, M:F = 1:1), 2) BMI > 30 kg/m2 (n = 40, M:F = 1:1), and 3) OSAS patients with BMI > 30 kg/m2 using nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment on an average > 4 h/d (n = 40, M:F = 1:1).
- Exclusion criteria: antimicrobial treatment within 3 months prior the baseline visit, inflammatory bowel diseases.
Course of the Study
- Baseline phase (3 weeks)
- Intervention phase (16 weeks)
- Follow-up phase (24 months)
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier (NCT number): NCT04850391
Duration of the study: Started 2021. Recruitment completed. Follow-up, analyses and reporting ongoing.
Principal investigator: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
Our knowledge of physiological causes of sleep apnoea has increased during the last decade. Positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy is not suitable for everyone and new treatment methods are needed. The Wello2® breathing exercise device would be an affordable and easy-to-use treatment for selected sleep apnoea patients of all ages.
Objectives of the study:
The aim of the study is to evaluate the effect of the Wello2® breathing exercise device as a treatment for sleep apnoea.
- The primary goal is the effect of the Wello2® breathing exercise device on polysomnography (PSG) parameters and sleep apnoea symptoms after 3 months of use.
- The secondary goal is to investigate the maintenance of the potential effects even after a 3-month follow-up period without the Wello2® breathing exercise device.
Study design:
A clinical follow-up study in sleep apnoea patients at the Pulmonary Clinic who are not using any other form of sleep apnoea treatment. The duration of the study is 6 months, of which the active phase with the Wello2® breathing exercise device is 3 months and the follow-up phase is 3 months after the end of treatment.
Duration of the study: 2021- Recruitment completed. The analysis and reporting of the data continues.
Principal investigator: PhD, adjunct professor Ulla Anttalainen
CPAP treatment is increasingly started for elderly sleep apnea patients. CPAP treatment is known to reduce daytime sleepiness and improve quality of life in some elderly people as well. Most sleep apnea studies have been done on middle-aged patients, and very little is known about sleep apnea in people over 75.
Aims of the study:
• Special features of the phenotype of elderly sleep apnea patients compared to younger patients
• Adherence to CPAP treatment and the factors affecting it in the elderly patients
• Gender differences and differences in the 70-80-year-old and over 80-year-old age groups
Study design:
The research design is a retrospective register study. The data is collected through the Auria Clinical Informatics and manually from the electronic medical records of patients aged 18 and older who received a sleep apnea diagnosis at Turku University Central Hospital between 2012 and 2019.
Duration of the study: 2021 – Analysis and reporting ongoing.
Principal investigator: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
According to the international recommendations and Finnish regulations, the CPAP treatment of sleep apnoea patients should be monitored. The growing number of patients challenges healthcare resources. There is no data on how and how often patients should be followed-up and who particularly benefits from the follow-up. In monitoring, attention has been paid to patients whose adherence to treatment is poor. However, based on clinical experience, there are patients who use CPAP therapy for an average of 9 hours/day or more, but the reasons for this are unknown.
Aims of the study:
• To identify patients whose follow-up could be carried out
- based on questionnaires, wireless telemonitoring of CPAP treatment and capillary blood gases,
- 2) using the aforementioned and the nurse's telephone contact,
- 3) based on point 1) and an appointment at the nurse's outpatient office, or
- 4) based on point 1) and with the help of a doctor's appointment
• To establish criteria based on which patients could be segmented into groups requiring different levels of follow-up using point 1) mentioned above
Study design:
A retrospective registry study of CPAP-treated sleep apnoea patients (about 1,400 patients) coming to the 5-year follow-up of the Turku University Hospital lung clinic in 2019-2020, and patients using CPAP treatment for at least 9 h/day identified based on wireless remote monitoring of CPAP treatment.
Duration of the study: 2023- Analyses and reporting ongoing.
Principal investigator: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
Abnormal breathing during sleep increases daytime fatigue and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases, worsens the function of the endothelium of blood vessels and causes systemic inflammation. Patients with sleep apnoea have an increased post-operative risk for cardiovascular complications. However, sleep studies pre- and postoperatively have not been done in patients undergoing heart-lung machine-assisted surgery.
Research objectives:
- Does poor recovery from cardiac bypass surgery contribute to increased sleep-disordered breathing or does a pre-existing breathing problem contribute to poorer recovery from surgery.
- Does an already diagnosed sleep apnoea or other sleep disorder affect the recovery from the cardiac bypass surgery and vice versa, does the bypass surgery affect the patient's symptom profile.
- Are there some common factors between worsening sleep apnoea and coronary artery disease that explain the already known connection between these two diseases.
Study design:
The study design is a prospective, observational study. Patients (n= 70) coming for bypass surgery performed with the aid of a heart-lung machine are recruited for the study. Patients are examined for e.g. blood tests, ultrasound and polysomnography (PSG) before and after surgery; post-operative PSG will be performed 6 months after surgery.
Duration of the study: 2023 -. Recruitment, analysis and reporting in progress.
Principal investigator: Adjunct professor Jenni Toivonen
People with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have been reported to have more obstructive sleep apnoea and other sleep disorders than other women. Overweight is common in both PCOS and sleep apnoea patients, and both are associated with similar comorbidities of public health importance, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and dyslipidemia, the prevalences of which increase in the population with ageing and after menopause in women. It has been suggested that PCOS and sleep apnoea form a vicious circle, and treatment of sleep apnoea might benefit fertility, metabolism and reduce long-term morbidity in PCOS patients of childbearing age.
Research objectives:
To study
- how many of the women with sleep apnoea examined at the Pulmonary Diseases Clinic of Turku University Hospital have been diagnosed with PCOS?
- how many of the women with sleep apnoea examined at the Pulmonary Diseases Clinic have experienced involuntary infertility and/or symptoms suggestive of PCOS?
- how common is sleep apnoea in Finnish PCOS patients?
- is sleep apnoea associated with involuntary infertility?
- does CPAP treatment affect the menstrual cycle of PCOS patients with sleep apnoea and/or the treatment prognosis of fertility treatments?
Study design:
The main arms of the project consist of a retrospective observational cohort study, two survey studies, a national registry study, and a prospective intervention study.
Study duration: 2020 – Data collection ongoing.
Principal investigator: Professor Päivi Polo
The etiology of respiratory failure is diverse and patients often have multiple illnesses. We were the first in the Nordic countries to start wireless telemonitoring of bi-level ventilation in 2018.
Objectives:
To study
- diagnosis distribution of patients using bi-level ventilation
- co-occurrence and prognosis of diseases causing respiratory failure
- effectiveness of wireless teleonitoring of bi-level ventilation
- reasons for discontinueing bi-level ventilation
Study design:
Retrospective registry study. Patients who started bi-level ventilation at the the pulmonary clinic of Turku University Hospital in 2004-2014 (N = 1281) and in 2019-2021. Data related to respiratory failure and co-morbidities are manually collected from the electronic medical records.
Duration of the study: 2015- Analysis and reporting ongoing.
Principal investigator: Adjunct professor Ulla Anttalainen
The success of the initial phase of CPAP treatment and bi-level ventilation treatment has a significant impact on treatment adherence, and good face-to-face guidance from the nurse has been considered important. There are no publications about the initiation of CPAP treatment by the patient independently using only written instructions or videos.
The consulting respiratory care nurse started working at Turku University Hospital in 2018. The nurse starts bi-level ventilation for a patient in a non-pulmonary department and monitors it via a wireless remote monitoring program. If the treatment of respiratory failure started in this way is successful at the same time as treating a disease in another specialty, a treatment period in the pulmonary department is avoided. The consulting respiratory care nurse also takes care of e.g. about wireless telemonitoring of bi-level ventilation during the first months of treatment.
Objectives:
- Does self-initiation of CPAP treatment save the nursing staff's time?
- Does self-initiation of CPAP treatment affect treatment adherence and patient satisfaction?
- Does self-initiation of CPAP treatment affect the total costs compared to conventional CPAP initiation?
- Will there be savings in hospitalization days and costs due to the service of the consulting respiratory failure nurse, taking into account the increased salary costs caused by the consulting nurse?
Study design:
Retrospective register study. Consecutive patients who started CPAP treatment in 2021 (N=800) and adult patients who started 2PV treatment in Turku University Hospital in 2019-2021.
Duration of the study: 2022- Analysis and reporting ongoing.
Principal investigator: Professor Tarja Saaresranta
In the treatment of narcolepsy patients, much has been focused on the treatment of hypersomnia. Parasomnias and psychiatric symptoms have received little attention, although their impact on functional ability and quality of life is significant.
Study design:
We study the prevalence and quality of parasomnias (such as nightmares, sleep paralysis, parasomnias) in narcolepsy patients and their relationship to psychiatric symptoms (depression, anxiety), stage and severity of the disease, medication, and functional capacity and quality of life.
Research objectives:
- Develop treatment practices for this patient group
- Improves the quality of life of narcolepsy patients and their ability to work and study
- Increase awareness of sleep problems among professionals treating patients in order to organize comprehensive treatment
Duration of the study: 2021- . Recruitment comleted. Analysis and reporting continue.
Principal investigator: Adjunct professor Katja Valli